Human Siglec-2/CD22 LlaMABodyTM Bivalent VHH HuIgG2 Fusion Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # LMAB107321
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody. Bivalent Llama VHH domain, Human IgG2 Fusion Antibody.

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Human
Applications
Immunocytochemistry, Immunohistochemistry
Label
Unconjugated
Antibody Source
Recombinant Monoclonal Llama VHH domain Clone # L007.2.5H
Product Summary
Immunogen
Chinese Hamster Ovary cell line CHO-derived human Siglec-2/CD22 as immunogen for bivalent Llama VHH-Human IgG2 Fusion Antibody
Asp20-Arg687
Accession # CAA42006.1
Asp20-Arg687
Accession # CAA42006.1
Specificity
Clone L007.2.5H is a bivalent Llama VHH-Human IgG2 Fusion Antibody that detects Siglec-2/CD22 in direct ELISAs. Antibody construct is depicted below.Human Siglec-2/CD22 SpecificLlama VHH domainLlama Hinge Human IgG2N-terminusC-terminus
Clonality
Monoclonal
Host
Llama
Isotype
VHH domain
Scientific Data Images
Siglec-2/CD22 in Human PBMCs.
Siglec-2/CD22 was detected in immersion fixed human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) using Llama Anti-Human Siglec-2/CD22 LlaMABodyTM Bivalent VHH HuIgG2 Fusion Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # LMAB107321) at 8 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using Anti-alpaca Alexa Fluor 594 (red) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. Staining was performed using our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.Siglec-2/CD22 in Human Tonsil.
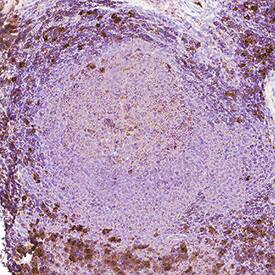
Siglec-2/CD22 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of Human Tonsil using Llama Anti-Human Siglec-2/CD22 LlaMABodyTM Bivalent VHH HuIgG2 Fusion Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # LMAB107321) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using anti-Llama secondaries with HRP and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm in lymphocytes. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Applications
Application
Recommended Usage
Immunocytochemistry
8-25 µg/mL
Sample: Immersion fixed human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs)
Sample: Immersion fixed human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs)
Immunohistochemistry
8-25 µg/mL
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of Human Tonsil
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of Human Tonsil
Please Note: Optimal dilutions of this antibody should be experimentally determined.
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Protein A or G purified from cell culture supernatant
Reconstitution
Reconstitute at 0.5 mg/mL in sterile PBS. For liquid material, refer to CoA for concentration.
Formulation
Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. *Small pack size (SP) is supplied either lyophilized or as a 0.2 µm filtered solution in PBS.
Shipping
The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. *Small pack size (SP) is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -20 to -70 °C
Stability & Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Siglec-2/CD22
References
- Crocker, P.R. et al. (2007) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7:255.
- Poe, J.C. and T.F. Tedder (2012) Trends Immunol. 33:413.
- Meyer, S.J. et al. (2018) Front. Immunol. 9:2820.
- Wilson, G.L et al. (1991) J. Exp. Med. 173:137.
- Stamenkovic, I. and B. Seed (1990) Nature 345:74.
- Collins, B.E. et al. (2004) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 101:6104.
- Crocker, P.R. and A. Varki (2001) Immunology 103:137.
- Ravetch, J.V. and L.L. Lanier (2000) Science 290:84.
- Wienands, Y.J. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:18769.
- Pluvinage, J.V. et al. (2019) Nature. 5568:7751.
- Clark, E.A. et al. (2018) Front. Immunol. 9:2235.
Long Name
Sialic Acid Binding Ig-like Lectin 2
Alternate Names
BL-CAM, CD22, Siglec2
Gene Symbol
CD22
UniProt
Additional Siglec-2/CD22 Products
Product Specific Notices
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...