Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 APC-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB3628A

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 APC-conjugated Antibody
Detection of CD31/PECAM‑1 in Mouse Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry.
Mouse splenocytes were stained with Goat Anti-Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 APC-conjugated Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB3628A, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC108A, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Detection of CD31/PECAM‑1 in Rat Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry.
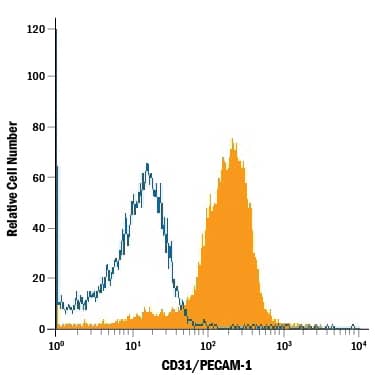
Rat splenocytes were stained with Goat Anti-Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 APC-conjugated Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB3628A, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC108A, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Detection of Mouse CD31/PECAM-1 by Flow Cytometry
CD31hiEmcnhi vessel and bone formation decreased during ageing but increased in bone regeneration. A, Representative images of CD31 (green), EMCN (red) and Osterix (white) immunostaining. Scale bar, 100 μm. G, growth plate. B, Quantification of CD31 and EMCN positive vessel volume in distal femora. C, Quantitative analysis of Osterix‐positive (OSX+) osteoprogenitors in distal femora. D and E, FACS analysis dot plot (D) and quantification (E) of CD31hiEMCNhi ECs. F, Representative images of CD31 (green) and EMCN (red) immunostaining in bone regeneration area after femoral trabecular bone ablation. Nuclei, DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 100 μm. G and H, Representative μCT images (G) and quantitative μCT analysis (H) of bone regeneration after femoral trabecular bone ablation. Selected areas for the measurements of bone volume (BV)/tissue volume (TV) were indicated with a yellow square. Data are shown as mean ± SD, (n = 6 in B, C, E and H). *P < .05; **P < .01 by one‐way ANOVA Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32080957), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 APC-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Mouse splenocytes and rat splenocytes
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using FAB3628A in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
Background: CD31/PECAM-1
PECAM-1 (Platelet-Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1), also known as CD31, is a 130 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein adhesion molecule in the immunoglobulin superfamily (1, 2). Expression is restricted to cells involved in circulation, especially endothelial cells, platelets, monocytes, neutrophils and lymphocyte subsets. PECAM-1 is concentrated at cell-cell junctions and is required for Transendothelial Migration (TEM) (1-3). The Extracellular Domain (ECD) of PECAM-1 has ten potential N-linked glycosylation sites and six C2-type Ig-like domains, the first of which is critical for adhesion and extravasation (3, 4). The cytoplasmic domain contains Immunoregulatory Tyrosine-based Inhibitory and Switch Motifs (ITIM, ITSM) that mediate both inhibition and activation via phosphotyrosine-mediated engagement of SH2-containing signaling molecules (1, 5). Metalloproteinase-mediated ectodomain shedding occurs during apoptosis (6) but increased serum PECAM-1 ectodomain in HIV and active multiple sclerosis occurs independent of apoptosis (7, 8). In humans, expression of six isoforms with exon deletions in the cytoplasmic domain is tissue- and stage-specific, but full-length PECAM-1 is predominant. A form lacking the ITSM predominates in mouse (9). Mouse PECAM-1 ECD shows 77%, 63%, 63%, 63%, and 61% amino acid (aa) identity with rat, human, canine, porcine, and bovine PECAM-1, respectively. PECAM-1 participates with other adhesion molecules in some functions, but is the critical molecule for TEM. Homotypic PECAM-1 adhesion in trans, combined with cycling of PECAM-1 to and from surface-connected endothelial cell vesicles, leads leukocytes across endothelial tight junctions (3, 10). Homotypic adhesion and signaling functions also strongly suppress mitochondria-dependent apoptosis (11). In platelets, PECAM-1 is necessary for limiting thrombus formation (12) and promoting integrin-mediated clot retraction and platelet spreading (13), but mechanisms for these phenomena are unclear. PECAM-/- mice are deficient in chemokine-mediated chemotaxis (14).
References
- Ilan, N. and J.A. Madri (2003) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15:515.
- Xie, Y. and W.A. Muller (1993) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:5569.
- Liao, F. et al. (1997) J. Exp. Med. 185:1349.
- Nakada, M.T. et al. (2000) J. Immunol. 164:452.
- Chemnitz, J.M. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 173:945.
- Ilan, N. et al. (2001) FASEB J. 15:362.
- Eugenin, E.A. et al. (2006) J. Leukoc. Biol. 79:444.
- Losy, J. et al. (1999) J. Neuroimmunol. 99:169.
- Wang, Y. et al. (2003) Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 284:H1008.
- Mamdouh, Z. et al. (2003) Nature 421:748.
- Gao, C. et al. (2003) Blood 102:169.
- Falati, S. et al. (2006) Blood 107:535.
- Wee, J.L. and D.E. Jackson (2005) Blood 106:3816.
- Wu, Y. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:3484.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional CD31/PECAM-1 Products
Product Documents for Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 APC-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 APC-conjugated Antibody
For research use only