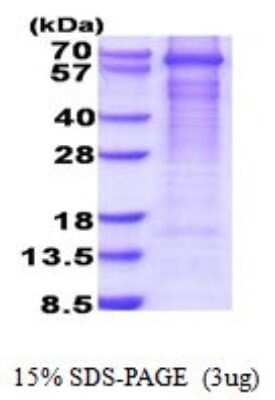
GAD1/GAD67: Proteins and Enzymes
Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase 1 (GAD1) also known as GAD67, is the enzyme responsible for the conversion of glutamic acid to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory transmitter in higher brain regions and putative paracrine hormone in pancreatic islets. GAD occurs as two molecular forms, 65 kDa and 67 kDa, that are encoded by separate genes and share 65% amino acid identity. GAD1 is highly conserved and is expressed in the CNS, pancreatic islet cells, testis, oviduct, and ovary. Abnormalities in GADs are related to several neurological disorders including epilepsy and schizophrenia. GAD2/GAD65 is an autoimmune target in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
6 results for "GAD1/GAD67 Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
6 results for "GAD1/GAD67 Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
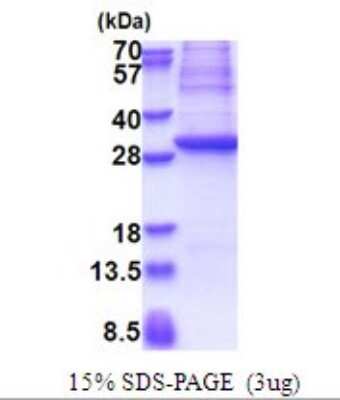
GAD1/GAD67: Proteins and Enzymes
Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase 1 (GAD1) also known as GAD67, is the enzyme responsible for the conversion of glutamic acid to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory transmitter in higher brain regions and putative paracrine hormone in pancreatic islets. GAD occurs as two molecular forms, 65 kDa and 67 kDa, that are encoded by separate genes and share 65% amino acid identity. GAD1 is highly conserved and is expressed in the CNS, pancreatic islet cells, testis, oviduct, and ovary. Abnormalities in GADs are related to several neurological disorders including epilepsy and schizophrenia. GAD2/GAD65 is an autoimmune target in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
| Applications: | PAGE |
| Applications: | PAGE |