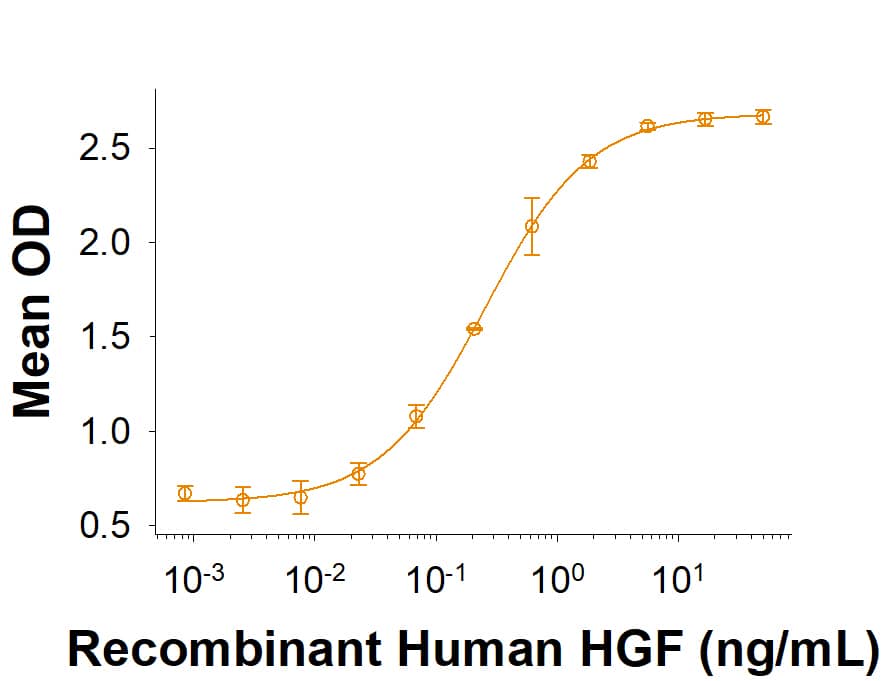
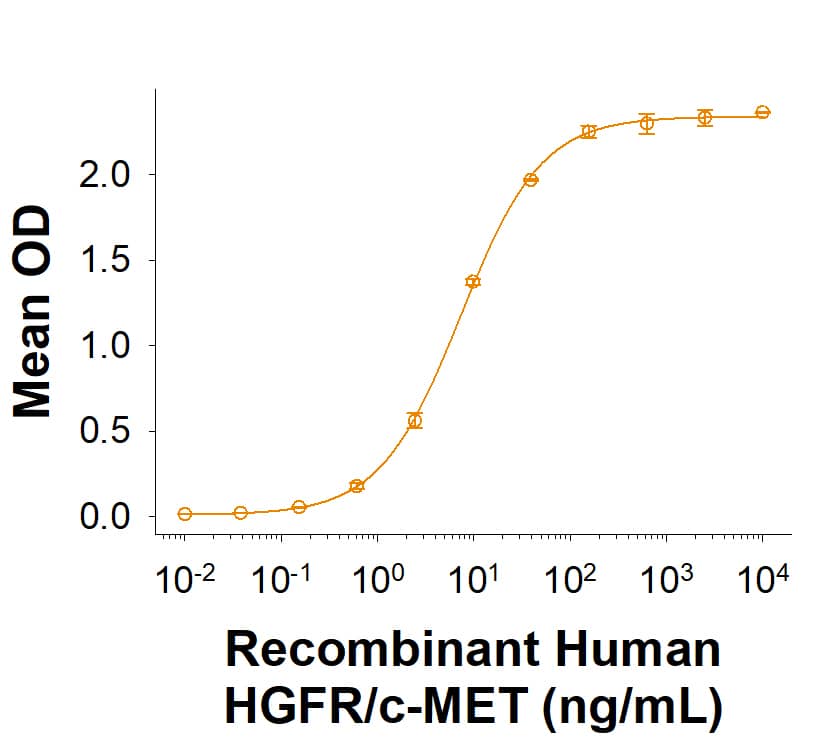
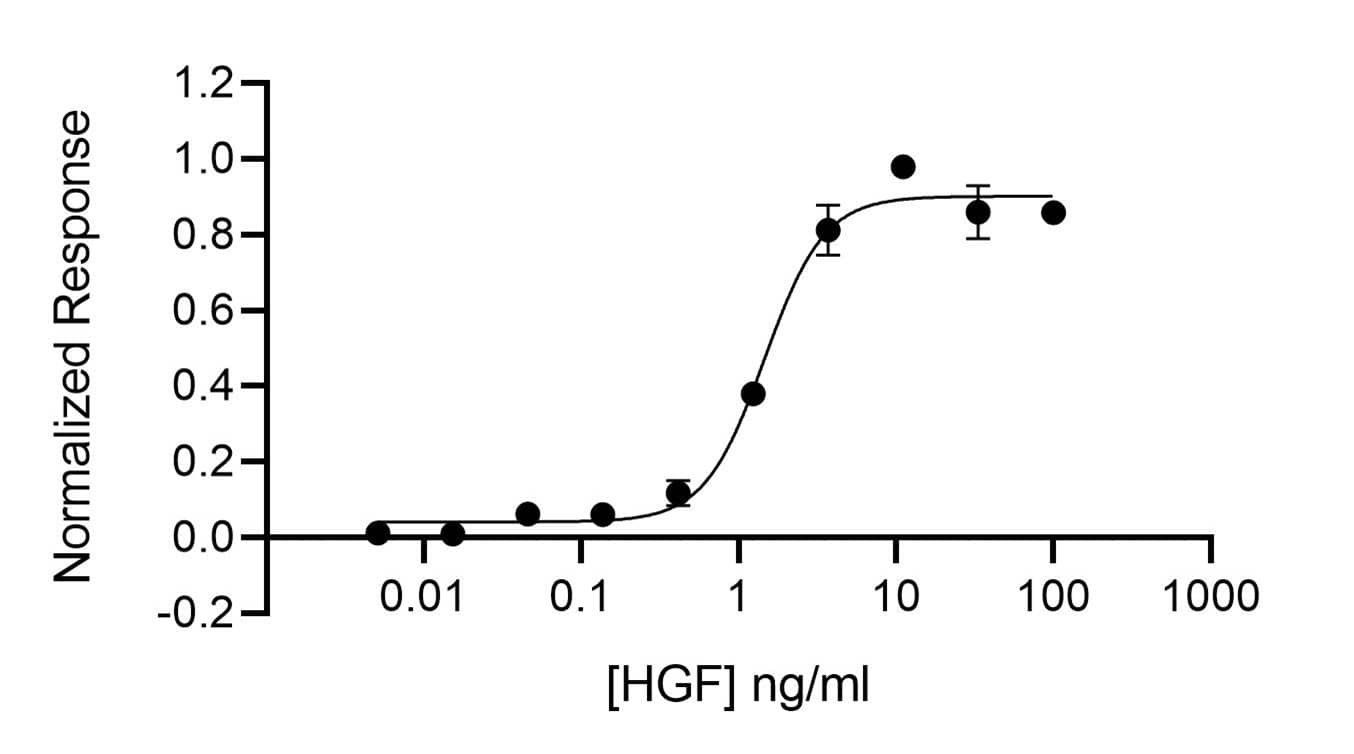
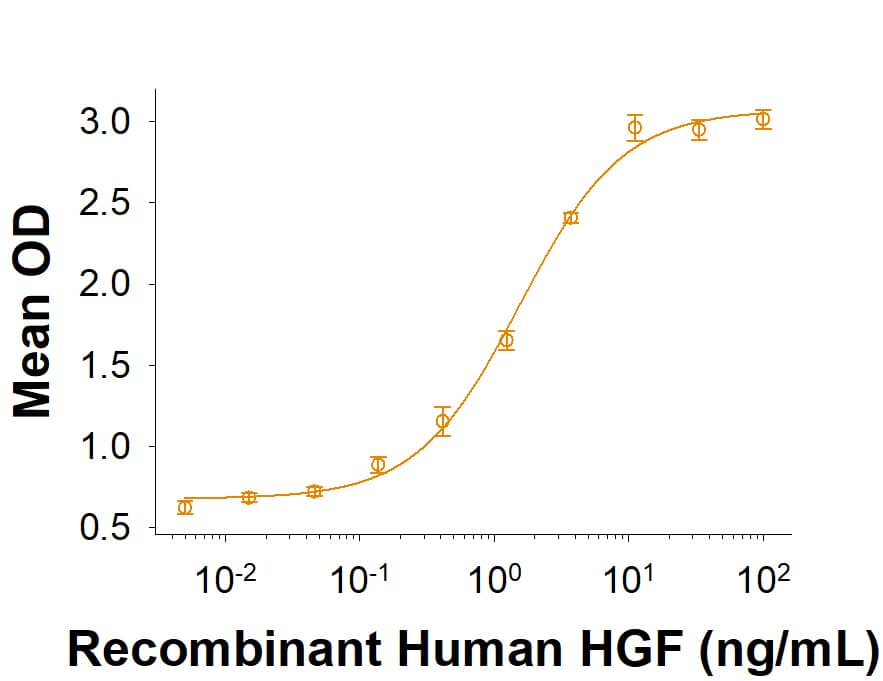
HGF: Proteins and Enzymes
HGF (Hepatocyte Growth Factor, Scatter Factor) induces the proliferation and migration of epithelial cells, hepatocytes, chondrocytes, keratinocytes, melanocytes, endothelial cells, and many tumor cells. During organogenesis and tissue repair, HGF promotes epithelial/endothelial morphogenesis by inducing cell scattering and branching tubulogenesis. It also supports insulin production by pancreatic beta cells, neuronal survival, and immune tolerance. HGF is secreted as a propeptide that is activated by uPA or HGF Activator at sites of tissue damage. Its signaling through the receptor HGF R/c-MET is enhanced by its prior binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. The serum levels of HGF are elevated in a wide range of pathologies including liver damage, acute kidney failure, myocardial infarction, type 1 diabetes, obesity, and cancer, as well as in the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients.
13 results for "HGF Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
13 results for "HGF Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
HGF: Proteins and Enzymes
HGF (Hepatocyte Growth Factor, Scatter Factor) induces the proliferation and migration of epithelial cells, hepatocytes, chondrocytes, keratinocytes, melanocytes, endothelial cells, and many tumor cells. During organogenesis and tissue repair, HGF promotes epithelial/endothelial morphogenesis by inducing cell scattering and branching tubulogenesis. It also supports insulin production by pancreatic beta cells, neuronal survival, and immune tolerance. HGF is secreted as a propeptide that is activated by uPA or HGF Activator at sites of tissue damage. Its signaling through the receptor HGF R/c-MET is enhanced by its prior binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. The serum levels of HGF are elevated in a wide range of pathologies including liver damage, acute kidney failure, myocardial infarction, type 1 diabetes, obesity, and cancer, as well as in the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients.
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q53WS5 |
| Applications: | BA, Bind |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | P14210.2 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | Sf 21 (baculovirus) |
| Accession #: | P14210.2 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | P14210.2 |
| Applications: | BA |
Biotinylated
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | P14210.2 |
| Source: | Sf 21 (baculovirus) |
| Accession #: | P14210 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P14210.2 |
| Applications: | BA |
Wild type
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | P14210.2 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | Sf 21 (stably transfected) |
| Accession #: | Q08048 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | Sf 21 (baculovirus) |
| Accession #: | Q867B7 |
| Applications: | BA, Bind |
| Applications: | PAGE |