Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF2105

Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Antibody
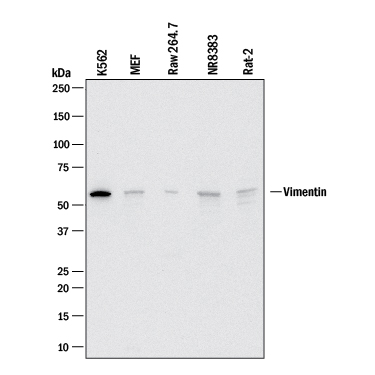
Detection of Human, Mouse, and Rat Vimentin by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line, MEF mouse embryonic feeder cells, RAW 264.7 mouse monocyte/macrophage cell line, NR8383 rat alveolar macrophage cell line, and Rat-2 rat embryonic fibroblast cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2105) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF017). A specific band was detected for Vimentin at approximately 55 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Western Blot Buffer Group 1.Vimentin in Human Skin.
Vimentin was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human skin using 10 µg/mL Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2105) overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained with the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.Vimentin in HeLa Human Cell Line.
Vimentin was detected in immersion fixed HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cell line using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2105) at 1.7 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to intermediate filaments in cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.Applications for Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Antibody
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed A549 human lung carcinoma cell line untreated or treated with 10 ng/ML TGF-beta (Catalog # 240-B) for 48 hours, and immersion fixed HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cell line
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human skin
Knockout Validated
Simple Western
Sample: K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line and Jurkat human acute T cell leukemia cell line
Western Blot
Sample: K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line, MEF mouse embryonic feeder cells, RAW 264.7 mouse monocyte/macrophage cell line, NR8383 rat alveolar macrophage cell line, and Rat‑2 rat embryonic fibroblast cell line
Reviewed Applications
Read 8 reviews rated 4.3 using AF2105 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
Background: Vimentin
Vimentin is a 57 kDa class III intermediate filament (IF) protein that belongs to the intermediate filament family. It is the predominant IF in cells of mesenchymal origin such as vascular endothelium and blood cells (1‑3). The human Vimentin cDNA encodes a 466 amino acid (aa) protein that contains head and tail regions with multiple regulatory Ser/Thr phosphorylation sites, and a central rod domain with three coiled-coil regions separated by linkers (1, 2). Human Vimentin shares 97‑98% aa identity with mouse, rat, ovine, bovine and canine Vimentin. Sixteen Vimentin coiled-coil dimers self-assemble to form intermediate (10‑12 nm wide) filaments (4). These filaments then anneal longitudinally to form non-polarized fibers that support cell structure and withstand stress (4). IF fibers are highly dynamic, and half-life depends on the balance between kinase and phosphatase activity. For example, phosphorylation followed by dephosphorylation drives IF disintegration, followed by reorganization during mitosis (1, 5, 6). Interactions of head and tail domains link IFs with other structures such as actin and microtubule cytoskeletons (7). Vimentin is involved in positioning autophagosomes, lysosomes and the Golgi complex within the cell (8). It facilitates cell migration and motility by recycling internalized trailing edge integrins back to the cell surface at the leading edge (9‑11). Vimentin helps maintain the lipid composition of cellular membranes, and caspase cleavage of Vimentin is a key event in apoptosis (8, 12). Phosphorylation promotes secretion of Vimentin by TNF-alpha -stimulated macrophages (13). Extracellular Vimentin has been shown to associate with several microbes, and appears to promote an antimicrobial oxidative burst (13, 14). Cell-associated Vimentin can also interact with NKp46 to recruit NK cells to tuberculosis-infected monocytes (15).
References
- Omary, M.B. et al. (2006) Trends Biochem. Sci. 31:383.
- Ivaska, J. et al. (2007) Exp. Cell Res. 313:2050.
- Ferrari, S. et al. (1986) Mol. Cell. Biol. 6:3614.
- Sokolova, A.V. et al. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:16206.
- Eriksson, J.E. et al. (2004) J. Cell Sci. 117:919.
- Li, Q.-F. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:34716.
- Esue, O. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:30393.
- Styers, M.L. et al. (2005) Traffic 6:359.
- McInroy, L. and A. Maata (2007) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 360:109.
- Nieminen, M. et al. (2006) Nat. Cell Biol. 8:156.
- Ivaska, J. et al. (2005) EMBO J. 24:3834.
- Byun, Y. et al. (2001) Cell Death Differ. 8:443.
- Mor-Vaknin, N. et al. (2003) Nat. Cell Biol. 5:59.
- Zou, Y. et al. (2006) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 351:625.
- Garg, A. et al. (2006) J. Immunol. 177:6192.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Vimentin Products
Product Documents for Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Antibody
For research use only




