CD57 Products
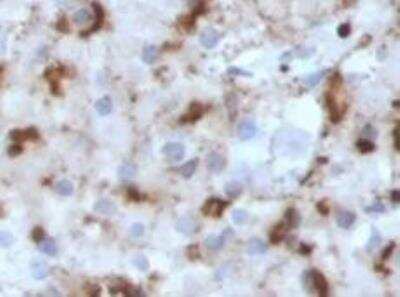
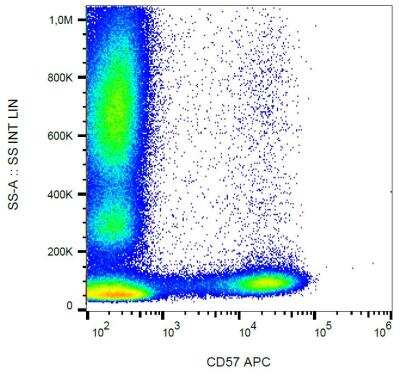
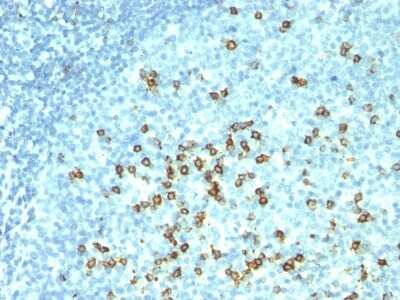
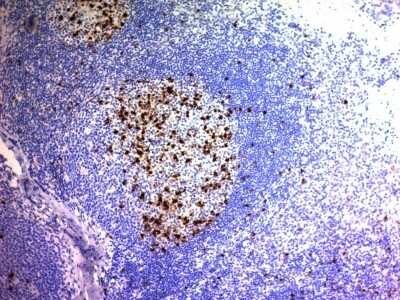
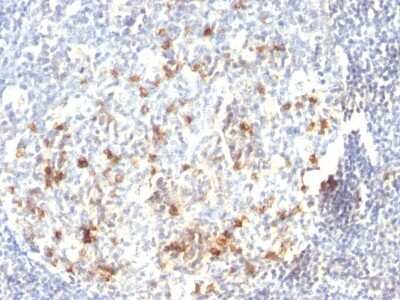
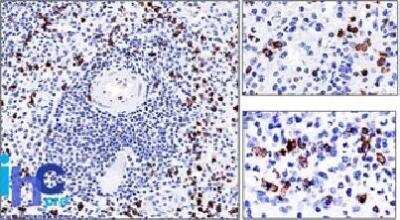
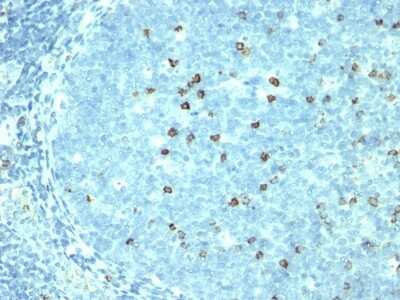
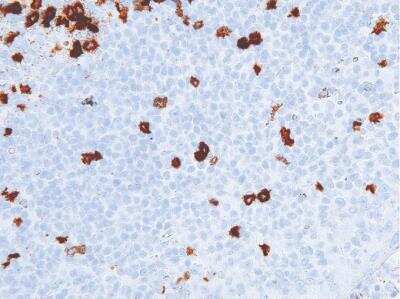
The CD57 antigen, also referred to as human natural killer-1 (HNK-1) and LEU-7, is a carbohydrate epitope containing sulfated glucuronic acid that is expressed by many cell types within the nervous system (1,2). Cellular expression of CD57 changes during progression of neural development (1). The CD57 epitope is synthesized by enzymes including a sulfotransferase and one of two glucotransferases (GlcAT-P or GlcAT-S) (1,2). The structure of the CD57/HNK-1 epitope consists of 3-O-sulfated glucuronic acid (GlcA) attached to a terminal galactose (HSO3-3GlcAbeta1-3Galbeta1-4GlcNAc-R) (1,2). The CD57 epitope was first identified and a marker for HNK cells and its expression is associated with NK cell maturation (1-3).
CD57 expression has become a common pathological marker. CD57+ CD8+ T cell expression is observed in various cancers and is often linked to reduced survival (3). On the other hand, CD57+ NK cell expression is associated with less severe disease and better prognosis in cancer patients (3). CD57 is also associated with immune dysfunction and autoimmune disease (3,4). For example, T cell immunosenescence is characterized by an upregulation of CD57 along with KLRG-1 and a loss of CD27 and CD28 expression (4). Expanded autoreactive T cells are also related to diseases including multiple sclerosis (MS) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (3). Conversely, reduced numbers of CD57+ NK cells and NK cell cytotoxicity is observed in various autoimmune diseases such as apoptotic dermatitis and sjogren's syndrome (3).
References
1. Focosi D, Bestagno M, Burrone O, Petrini M. CD57+ T lymphocytes and functional immune deficiency. J Leukoc Biol. 2010;87(1):107-116. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0809566
2. Morise J, Takematsu H, Oka S. The role of human natural killer-1 (HNK-1) carbohydrate in neuronal plasticity and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861(10):2455-2461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.06.025
3. Nielsen CM, White MJ, Goodier MR, Riley EM. Functional Significance of CD57 Expression on Human NK Cells and Relevance to Disease. Front Immunol. 2013;4:422. Published 2013 Dec 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2013.00422
4. Lian J, Yue Y, Yu W, Zhang Y. Immunosenescence: a key player in cancer development. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):151. Published 2020 Nov 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00986-z6
Show More
CD57 expression has become a common pathological marker. CD57+ CD8+ T cell expression is observed in various cancers and is often linked to reduced survival (3). On the other hand, CD57+ NK cell expression is associated with less severe disease and better prognosis in cancer patients (3). CD57 is also associated with immune dysfunction and autoimmune disease (3,4). For example, T cell immunosenescence is characterized by an upregulation of CD57 along with KLRG-1 and a loss of CD27 and CD28 expression (4). Expanded autoreactive T cells are also related to diseases including multiple sclerosis (MS) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (3). Conversely, reduced numbers of CD57+ NK cells and NK cell cytotoxicity is observed in various autoimmune diseases such as apoptotic dermatitis and sjogren's syndrome (3).
References
1. Focosi D, Bestagno M, Burrone O, Petrini M. CD57+ T lymphocytes and functional immune deficiency. J Leukoc Biol. 2010;87(1):107-116. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0809566
2. Morise J, Takematsu H, Oka S. The role of human natural killer-1 (HNK-1) carbohydrate in neuronal plasticity and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861(10):2455-2461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.06.025
3. Nielsen CM, White MJ, Goodier MR, Riley EM. Functional Significance of CD57 Expression on Human NK Cells and Relevance to Disease. Front Immunol. 2013;4:422. Published 2013 Dec 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2013.00422
4. Lian J, Yue Y, Yu W, Zhang Y. Immunosenescence: a key player in cancer development. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):151. Published 2020 Nov 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00986-z6
38 results for "CD57" in Products
38 results for "CD57" in Products
CD57 Products
The CD57 antigen, also referred to as human natural killer-1 (HNK-1) and LEU-7, is a carbohydrate epitope containing sulfated glucuronic acid that is expressed by many cell types within the nervous system (1,2). Cellular expression of CD57 changes during progression of neural development (1). The CD57 epitope is synthesized by enzymes including a sulfotransferase and one of two glucotransferases (GlcAT-P or GlcAT-S) (1,2). The structure of the CD57/HNK-1 epitope consists of 3-O-sulfated glucuronic acid (GlcA) attached to a terminal galactose (HSO3-3GlcAbeta1-3Galbeta1-4GlcNAc-R) (1,2). The CD57 epitope was first identified and a marker for HNK cells and its expression is associated with NK cell maturation (1-3).
CD57 expression has become a common pathological marker. CD57+ CD8+ T cell expression is observed in various cancers and is often linked to reduced survival (3). On the other hand, CD57+ NK cell expression is associated with less severe disease and better prognosis in cancer patients (3). CD57 is also associated with immune dysfunction and autoimmune disease (3,4). For example, T cell immunosenescence is characterized by an upregulation of CD57 along with KLRG-1 and a loss of CD27 and CD28 expression (4). Expanded autoreactive T cells are also related to diseases including multiple sclerosis (MS) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (3). Conversely, reduced numbers of CD57+ NK cells and NK cell cytotoxicity is observed in various autoimmune diseases such as apoptotic dermatitis and sjogren's syndrome (3).
References
1. Focosi D, Bestagno M, Burrone O, Petrini M. CD57+ T lymphocytes and functional immune deficiency. J Leukoc Biol. 2010;87(1):107-116. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0809566
2. Morise J, Takematsu H, Oka S. The role of human natural killer-1 (HNK-1) carbohydrate in neuronal plasticity and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861(10):2455-2461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.06.025
3. Nielsen CM, White MJ, Goodier MR, Riley EM. Functional Significance of CD57 Expression on Human NK Cells and Relevance to Disease. Front Immunol. 2013;4:422. Published 2013 Dec 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2013.00422
4. Lian J, Yue Y, Yu W, Zhang Y. Immunosenescence: a key player in cancer development. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):151. Published 2020 Nov 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00986-z6
Show More
CD57 expression has become a common pathological marker. CD57+ CD8+ T cell expression is observed in various cancers and is often linked to reduced survival (3). On the other hand, CD57+ NK cell expression is associated with less severe disease and better prognosis in cancer patients (3). CD57 is also associated with immune dysfunction and autoimmune disease (3,4). For example, T cell immunosenescence is characterized by an upregulation of CD57 along with KLRG-1 and a loss of CD27 and CD28 expression (4). Expanded autoreactive T cells are also related to diseases including multiple sclerosis (MS) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (3). Conversely, reduced numbers of CD57+ NK cells and NK cell cytotoxicity is observed in various autoimmune diseases such as apoptotic dermatitis and sjogren's syndrome (3).
References
1. Focosi D, Bestagno M, Burrone O, Petrini M. CD57+ T lymphocytes and functional immune deficiency. J Leukoc Biol. 2010;87(1):107-116. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0809566
2. Morise J, Takematsu H, Oka S. The role of human natural killer-1 (HNK-1) carbohydrate in neuronal plasticity and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861(10):2455-2461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.06.025
3. Nielsen CM, White MJ, Goodier MR, Riley EM. Functional Significance of CD57 Expression on Human NK Cells and Relevance to Disease. Front Immunol. 2013;4:422. Published 2013 Dec 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2013.00422
4. Lian J, Yue Y, Yu W, Zhang Y. Immunosenescence: a key player in cancer development. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):151. Published 2020 Nov 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00986-z6
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat (Negative) |
| Details: | Mouse IgM Kappa Monoclonal Clone #SPM129 |
| Applications: | IHC, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgM Monoclonal Clone #TB01 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat (Negative) |
| Details: | Mouse IgM Kappa Monoclonal Clone #HNK-1 + NK-1 |
| Applications: | IHC, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat (Negative) |
| Details: | Mouse IgM Kappa Monoclonal Clone #NK/804 |
| Applications: | IHC, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat (Negative) |
| Details: | Mouse IgM Kappa Monoclonal Clone #HNK-1 or Leu-7 |
| Applications: | IHC, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat (Negative) |
| Details: | Mouse IgM Kappa Monoclonal Clone #NK-1 |
| Applications: | IHC, ICC/IF, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat (Negative) |
| Details: | Mouse IgM Kappa Monoclonal Clone #SPM527 |
| Applications: | IHC, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgM Kappa Monoclonal Clone #IHC539 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #NK1/7565 |
| Applications: | IHC |